The Data Pool is the information source for the organization's AI Chatbot.
SysAdmins and AI admins can use the Data Pool data to customize the Copilot’s Language Models (LLMs) for end users' specific needs.
The Data Pool consists of Datasets—containers that SysAdmins add and configure to enhance SysAid Copilot’s knowledge and personalize responses to user queries. These include:
Service Record Data
Q&A Sets
Knowledge Base Articles
Documents
URL
SharePoint
AI Agent
Requirements:
SysAdmin or AI Admin permissions.
SysAdmins and AI admins can manage datasets and their sources within the Data Pool section.
To access and manage the Data Pool, go to Settings > SysAid Copilot > Data Pool, or click the 3-dot menu in the top right corner of the Agent chatbot and select Data Pool.
The Data Pool Page consists of two main sections:
Data Pool side panel
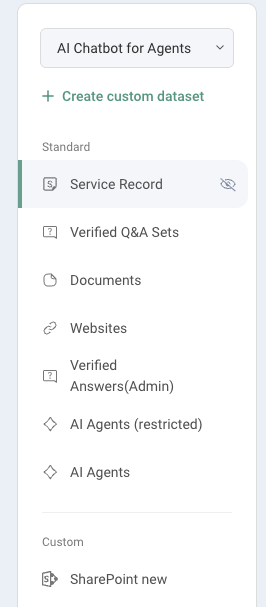
Here you can select which chatbot’s data pool you’d like to edit and see all available datasets for the selected chatbot. Standard datasets are fixed within the system, and you can create custom datasets to fit your organization’s needs.
Standard datasets
Type | Description |
Service Record | Includes all closed incident service records that were created or updated within the selected time period. By default, this includes service record data from the last 2 years. |
Knowledge Base | Syncs all articles from your SysAid Knowledge Base. By default, all users can access all articles unless access is limited in the dataset configuration. |
Verified Q&A Sets | Includes query-and-answer pairs that were verified in the Monitor & Fine-tune section. Verified pairs are automatically added to the standard Q&A dataset. |
Documents | Includes uploaded files such as PDFs, Word documents, Excel sheets, CSVs, and PowerPoint presentations. Maximum file size: 100MB. |
Websites | Includes content from publicly accessible websites only. Password-protected or sign-in-required sites are not supported. Sites are crawled once at the time of addition. To refresh the content, remove and re-add the site. |
SharePoint | Includes connected SharePoint files with automatic sync every 10 minutes. By default, all users can access all content unless access is restricted in the dataset configuration. |
AI Agent | Includes only published AI agents. Newly published agents are automatically added to the standard AI Agents dataset. |
Dataset content
Dataset actions and overview
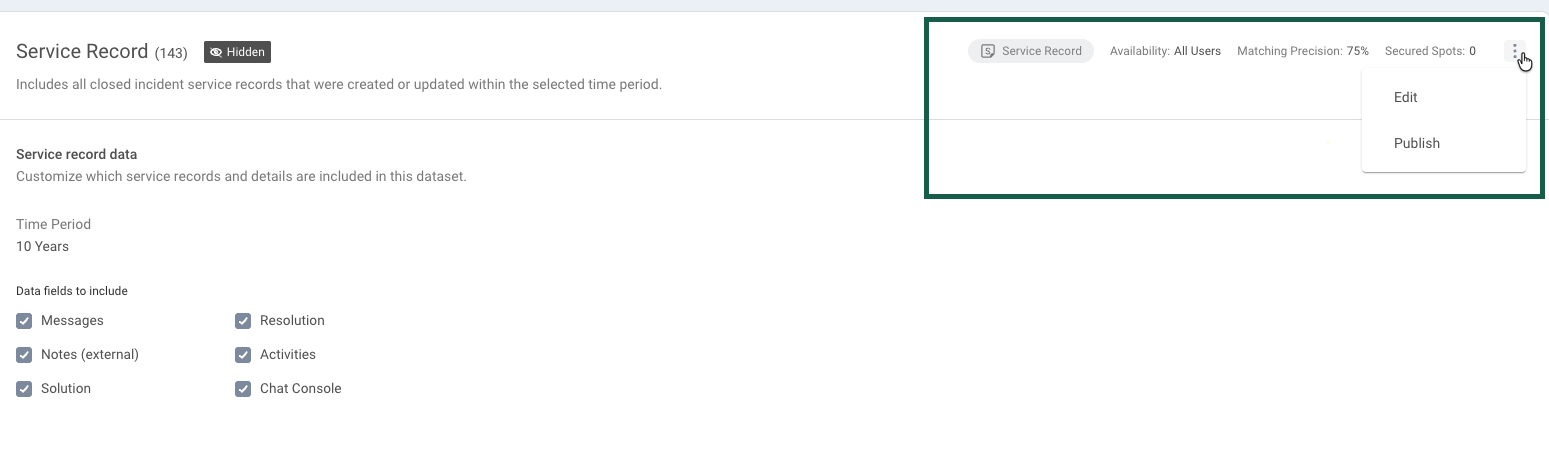
The title of the dataset can be edited - simply click the 3-dot menu to the left to change its name. Next to the title, you can see the number of items included in this dataset.
Each dataset includes a label showing its type and a summary panel in the top right corner that shows key information about its status and relevance:
Availability: Defines which users can access the dataset (e.g., “All Users” or restricted groups).
Matching Precision: Determines how strictly a dataset must match a user’s query before the chatbot prioritizes it. This score ranges from 0% to 100% and helps Copilot assess data relevance.
Secured Spots: Displays the number of dataset references that should always be considered when generating a response, taking matching relevance into account as well.
These indicators help you quickly understand who has access to a dataset and how it performs in AI-driven conversations.
You can configure these details, along with settings relevant to the specific dataset type, by clicking the 3-dot menu in the top-right corner.
From here, you can:
Publish or Hide a dataset to control whether it’s an active part of the Data Pool.
Edit its access and relevance settings to adjust how and when the data is used. Learn more about Dataset permissions and advanced settings.
These quick actions help you manage your datasets directly from the Data Pool without needing to open their full configuration.
Most datasets also include a search bar right above the items list that allows you to search items by name. In the AI agent dataset, you can also search by the AI agent’s job description.
To learn how to create and edit a dataset, see Creating a Dataset.