Welcome to SysAid Remote Control!
As an IT administrator and helpdesk technician, there is always far too much work to do, and much of it is spread out over a large geographic area. From multi-storey offices to work-from-home employees to offsite servers, in order to properly care for your IT environment, you need to be everywhere at once. While the average person can only be in one place at any one time, SysAid Remote Control allows you to provide service to everywhere from whereever you are.
Log into SysAid from any computer with an internet connection and perform a remote control session to any of your users, anywhere, anytime. Alternatively, perform a remote control session within a closed LAN (no internet access), or use our SaaS solution, SysAid Cloud Edition, to perform a remote control session directly from the cloud. Not near a computer?
Once you are logged in, you can perform a remote control session from many different places within SysAid. Initiate remote control from:
The asset page for any computer asset in SysAid
From within a chat session
From a ticket
From the list of online users
With SysAid Remote Control, accessing remote computers and remotely assisting users has never been easier!
Types of remote control
SysAid has three primary methods of remote control:
In-browser remote control using HTML 5 and the SysAid Remote Control Gateway (RCG)
Peer to peer remote control in a dedicated window (referred to in SysAid as a direct connection)
Attended or unattended sessions using SysAid TeamViewer Embedded service
Please read more about the differences between these remote control methods below.
Prerequisites for SysAid Remote Control
There are three general prerequisites that must be met before you can initiate a remote control session:
The SysAid agent must be installed on the target computer and the computer must be reporting to the SysAid server.
The SysAid agent on the target computer must be configured to allow remote control (done at time of deployment).
Remote control to the target computer must be enabled (see Additional RC Settings below) on the SysAid server.
There are additional requirements that must be met for the different RC methods:
Remote control using RCG
In-browser remote control uses HTML 5 and the SysAid Remote Control Gateway. To use this RC method:
Your browser must support HTML 5.
The SysAid agent on the target computer must be updated to the latest version. Using RCG is supported in version 8.0 of SysAid and higher.
You must have an available RC license.
The computer initiating RC and the target computer must both have access to the RCG server (by default the SysAid server) over port 443 and 8443.
SysAid comes with one concurrent user license for using RCG. If this license is in use, you must wait until the previous RCG session has ended before beginning a new one. If you would like to order additional licenses for RC, please contact SysAid Sales.
Peer to peer remote control
Peer to peer remote control opens in a dedicated window. To use this RC method:
You must have installed the SysAid RC Tools on the computer from which you will perform the remote control session. The RC Tools are installed automatically when you install the Administrator Tools. You may find the Administrator Tools under Settings > Network Discovery > Downloads.
The computer that you are using to perform the RC session must have an IP address that's accessible to the target computer.
Please note:
There is no license limit for the number of concurrent peer to peer RC sessions.
Initiating a Remote Control session
There are many places within SysAid that you can initiate a remote control session. These are detailed below. You must also choose your remote control method, and you may need approval if a user is logged into the machine already.
Before initializing the RC session:
Choose your remote control Method. Method is RCG or direct connection (peer to peer). Also, if there are one or more users logged in to the machine, a drop-down list of user sessions will appear, and you can choose which session you would like to connect to. If there are no users logged in to the target machine, you will connect directly and be able to log in normally with a valid username and password.
Approving the RC session:
If there is a user logged into the target computer and remote control confirmation is enabled, the end user must approve the remote control session. This is done by means of a popup window the end user sees.
Popup on end user's computer allowing them to accept or refuse a remote control session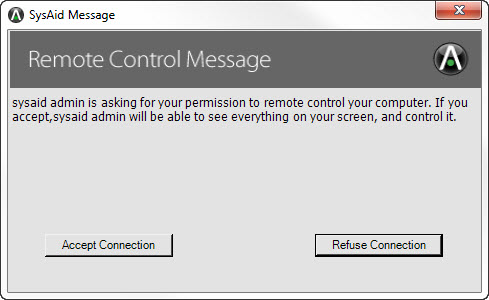
Places from which you can initiate remote control:
RC tab on asset form
Go to Assets > Asset Management > Asset List and click on the desired asset to open the asset form. Then open the RC tab.
Select your desired remote control method and click Start to initiate your remote control session. Note that SysAid only shows available remote control options.
Start a remote control session from the RC tab on the asset form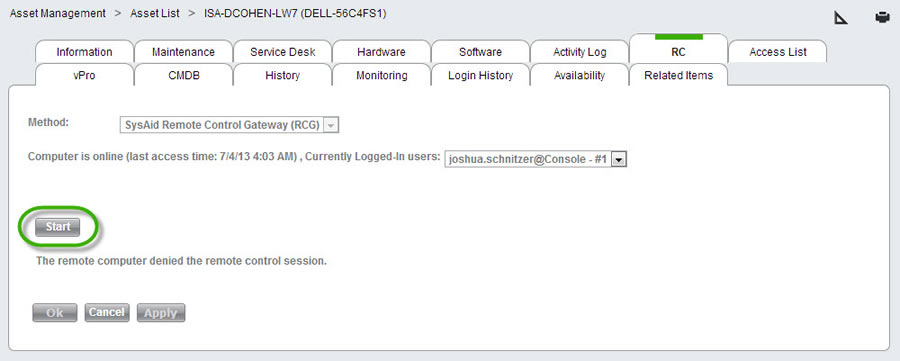
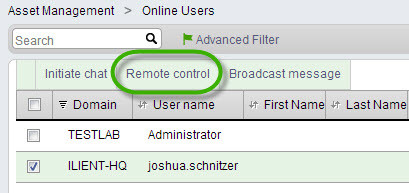
Online Users list
Go to Assets > Asset Management > Online Users.
Select the session you would like to connect to by clicking the tickbox at the left end of the row.
Click the Remote Control list option, to begin the remote control session.
Service Record
On the SR form, you may perform a remote control session from the Main Asset, Submit user, and Request user fields. Note that in order to initiate RC using either the Submit or Request user fields, the selected user must appear as the owner for an asset (Owner is one of the fields on the asset form). The remote control session will then be initiated to the owned asset even if it is not the same as the Main Asset for the service record.
Perform a remote control session from the SR form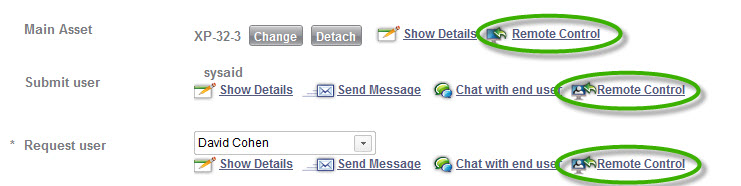
Chat
You can initiate a remote control session directly from a chat, giving you the ability to provide a quick solution to the problem at hand.
Click Remote Control on the General details panel in the top right corner of the screen.
Initiating remote control from a chat session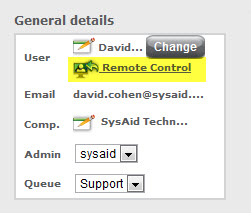
Using Remote Control
The SysAid remote control interface varies depending upon the chosen remote control method.
Remote control using RCG
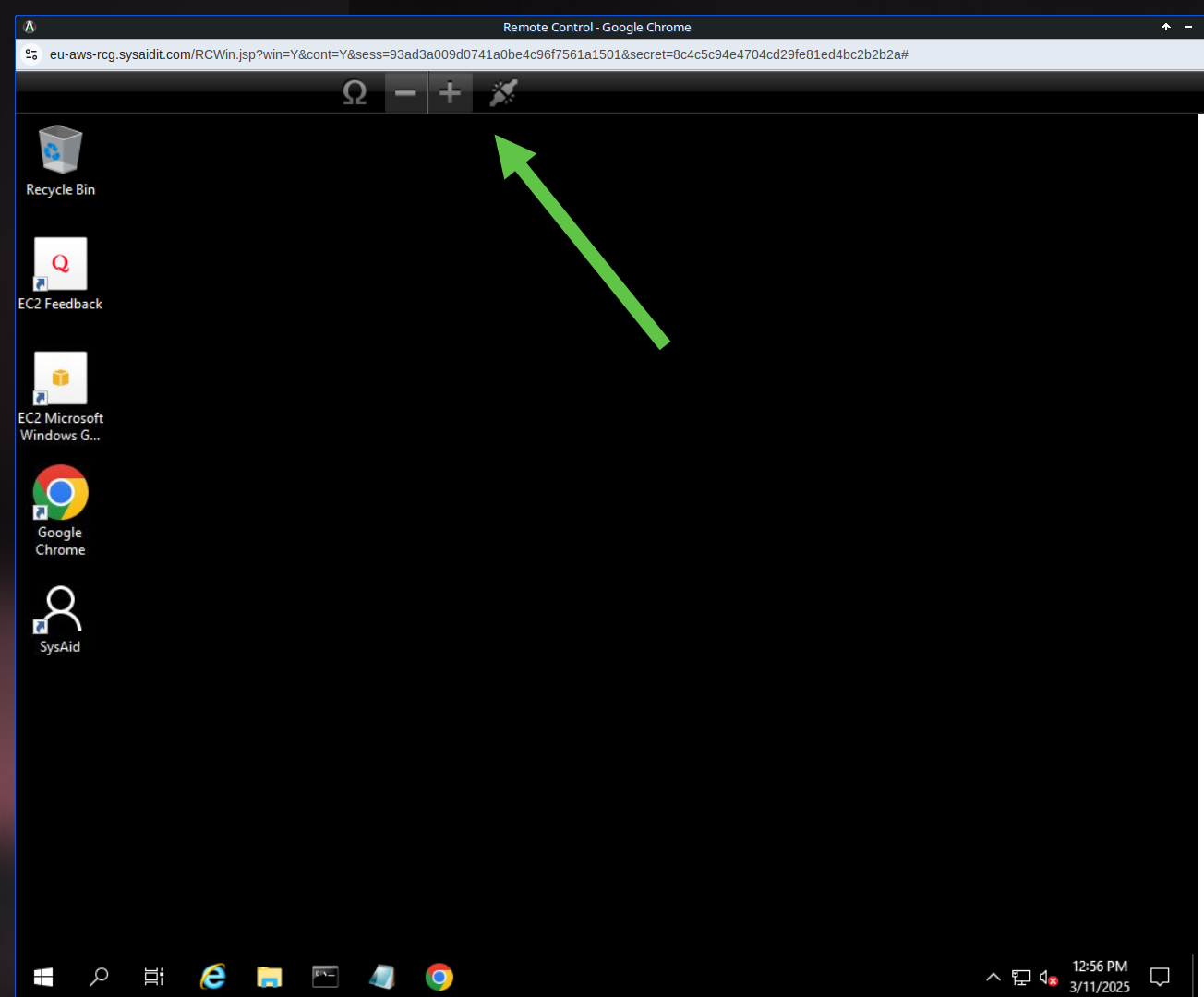
When using RCG, the remote control session opens in your browser window. Controlling the remote control session is easy:
Left click and right click work normally.
Typing works normally.
Click and drag the end user's screen to move around the visible portion of the screen (if their screen is not completely visible within the window).
To click and drag something on the end user's screen, such as a scroll bar, you must left click and hold for two seconds, and then you may drag whatever you've clicked on. If you hold for less than two seconds before you start dragging, you will move the visible portion of the screen as described in the previous bullet point.
Additionally, there are four icons that appear above the end user's screen:
Icon | Description |
|---|---|
| Opens a list of special key combinations that you can send to the remote computer such as CTRL + ALT + DEL. |
| Allows you to shrink or enlarge the end user's screen within the RC window. |
| Opens the RC session in fullscreen view. |
| Disconnect from the RC session. This icon only appears in fullscreen mode. |
Peer to peer remote control
When using peer to peer remote control, the remote control session opens in a dedicated window.
You may work within this window exactly as you would work on your own computer, with one exception: for special key combinations such as CTRL + ALT + DEL, you must use the icons that appear above the end user's screen.
Additional Remote Control settings
There are several remote control settings that can have a significant impact on the way SysAid remote control performs.
Agent remote control settings
The SysAid agent, deployed to each computer in your network, contains some of the settings for remote control. Unlike most SysAid settings, these settings are stored locally on the computer with the agent installed, and not on the SysAid server. These settings are configured before deploying the agent. Once the agent has been deployed, the easiest way to change these settings is to redeploy the agent.
You may edit these settings either from Settings > Network Discovery > Deploy Agents or from within the Deployment tool, part of the Administrator Tools. Please note that you must make changes to these settings before deploying the agent. If you change these settings after deploying the agent, you must redeploy the agent for them to take effect.
Please note:
As these settings are stored locally per computer, they can be different for each of the computers in your network.
Remote control settings stored locally on the computer with the agent installed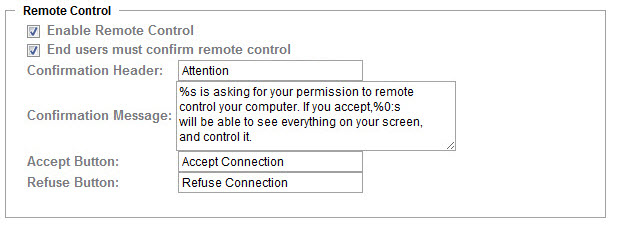
Enable Remote Control
If this option is unchecked, the remote control component will be uninstalled from the agents and remote control will not be possible to the selected computer.
Please note:
If you wish to uninstall the remote control component from your agents, create a new agent settings policy with this option unchecked. Then follow the steps detailed here to make sure this policy takes affect.
End users must confirm remote control
If there is no user logged into a computer at the time an RC session is initiated, this setting has no effect. If this setting is checked and there is a user logged in, the user must confirm the RC session. If the user declines, the RC session does not occur. If this setting is unchecked, an administrator can take control of a user's computer without their permission, even if they are using it.
Confirmation header
This is the header of the confirmation message that appears to the end user if they must confirm a remote control session.
Confirmation message
This is the body of the confirmation message that appears to the end user if they must confirm a remote control session.
Accept button
On the end user confirm RC message, this is the text that appears on the button that accepts the remote control session.
Refuse button
On the end user confirm RC message, this is the text that appears on the button that refuses the remote control session.
General remote control settings
Go to Settings > Asset Management > Remote Control Settings to see general remote control settings.
Please go here for a full description of all the options detailed on this page.
How SysAid Remote Control works
This section has two parts. The first two discuss how remote control works using RCG and the second explains peer to peer.
Important:
If you have lengthened the agent refresh interval (the amount of time the agent waits before contacting the SysAid server) beyond the default 30 seconds, you may need to wait an extended period of time before a remote control session is initiated.
Remote control using RCG
SysAid includes the SysAid Remote Control Gateway, which allows you to easily initiate a remote control session with any computer without needing to open any additional ports on the end user or administrator sides.
When you initiate a remote control session using RCG, the following steps occur:
The administrator sends a request to the SysAid server to initiate a remote control session with a target computer.
If the target computer is on the same LAN as the SysAid server, the SysAid server immediately sends a remote control request to the computer.
If the target computer is not on the same LAN as the SysAid server, the SysAid server relays the RC request the next time the agent on the target computer contacts the SysAid server. By default, this occurs every 30 seconds*.
If there is no user logged in to the target computer, or if a user is logged in but remote control confirmation is disabled, the remote control session is approved.
If a user is logged in to the target computer and remote control confirmation is enabled, the user receives a popup asking to confirm remote control. If the user confirms, the remote control session is approved. If the user declines, the remote control request is terminated.
After approval, the target computer initiates a remote control session with the SysAid server using SSL.
The SysAid RCG then relays the remote control session to the administrator's computer using SSL HTML 5. The remote control session opens in the administrators web browser.
Once the remote control session is established, both the administrator's computer and the target computer communicate with each other via the Remote Control Gateway.
Both the admin's computer and the target computer connect to the SysAid server using port 443, which is open by default. This means that even if there is a firewall between the administrator and the target computer, or between the SysAid server and either of the other two computers, there is never any need to open ports. As long as both computers have access to the SysAid server's IP address, remote control using RCG can be initiated with the click of a single button.
Important:
If you have lengthened the agent Refresh Interval (the amount of time the agent waits between each time it contacts the SysAid server) beyond the default 30 seconds, you may need to wait an extended period of time before a remote control session is initiated.
Remote control using the SysAid Remote Control Gateway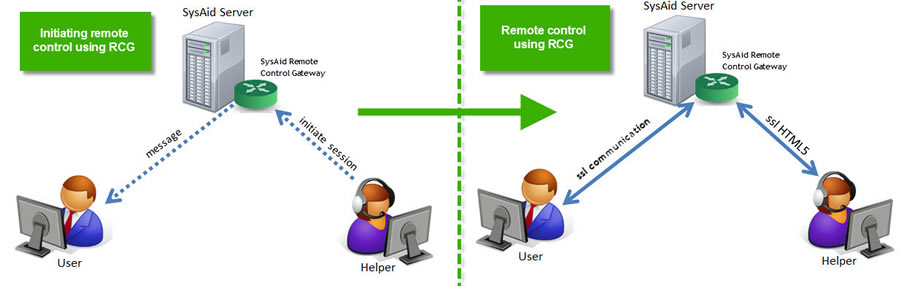
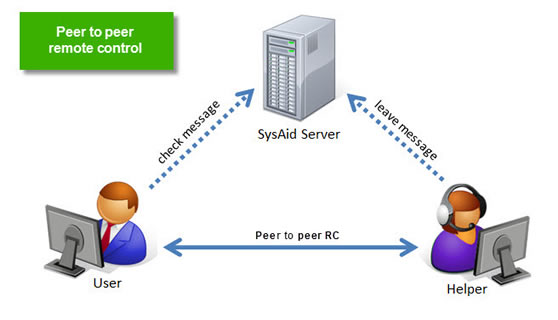
Peer to peer remote control
SysAid also supports peer to peer remote control for a direct remote control connection between computers.
When initiating a remote control session using peer to peer, the following steps occur:
The administrator sends a request to the SysAid server to initiate a remote control session with a target computer.
The SysAid server relays the RC request the next time the agent on the target computer contacts the SysAid server. By default, this occurs every 30 seconds*.
If there is no user logged in to the target computer, or if a user is logged in but remote control confirmation is disabled, the remote control session is approved.
If a user is logged in to the target computer and remote control confirmation is enabled, the user receives a popup asking to confirm remote control. If the user confirms, the remote control session is approved. If the user declines, the remote control request is terminated.
After approval, the target computer initiates a remote control session directly to the administrator's computer on the chosen port. This requires that the selected port be open and that the administrator's computer have an IP address accessible to the target computer.
The remote control session opens in the RC Tools viewer that's included in the Administrator Tools (see Prerequisites for Remote Control, above).
Once the remote control session is established, the computers communicate directly with no additional contact with the SysAid server.
Because the target computer initiates a remote control session, there is no need to open any ports on the side of the target computer. However, the target computer must be able to connect to the administrator's computer. Therefore, if there is a firewall on the administrator's end, you must open the appropriate port in order to allow communication. Furthermore, if there is a NAT on the administrator's end and there is no external IP address, you must set up port forwarding from the port chosen for RC to the administrator's local IP address.
For these reasons, remote control using RCG is simpler and is the preferred solution over peer to peer remote control.
Important:
If you have lengthened the agent Refresh Interval (the amount of time the agent waits between each time it contacts the SysAid server) beyond the default 30 seconds, you may need to wait an extended period of time before a remote control session is initiated.
Peer to peer remote control